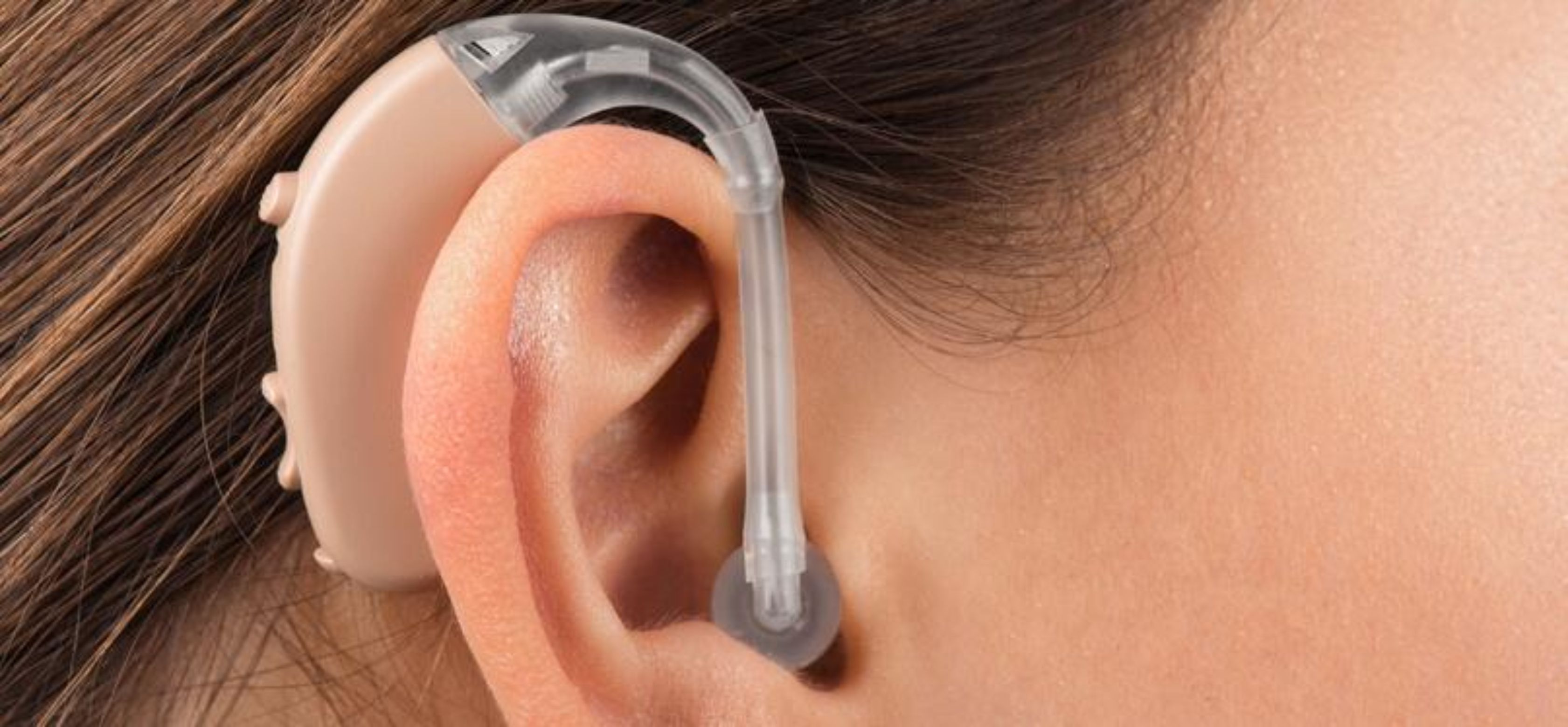
An audiologist is a healthcare professional who specializes in the diagnosis, treatment, and management of disorders related to hearing and balance. Audiologists are trained to assess and address a wide range of auditory and vestibular (balance-related) issues affecting individuals of all ages.
Roles and Responsibilities of Audiologists:
Diagnostic Evaluations: Audiologists conduct thorough assessments to evaluate hearing sensitivity and auditory function using various tests such as audiometry, tympanometry, and speech testing. They also assess vestibular function to diagnose balance disorders.
Treatment Planning: Based on diagnostic results, audiologists develop personalized treatment plans tailored to each patient's needs. This may include recommending hearing aids, assistive listening devices, cochlear implants, or providing auditory rehabilitation therapy.
Hearing Aid Services: Audiologists specialize in selecting, fitting, and dispensing hearing aids. They educate patients on how to use and maintain their devices effectively.
Tinnitus Management: Audiologists evaluate and provide management strategies for tinnitus (ringing or buzzing in the ears), which may include counseling, sound therapy, and devices designed to alleviate symptoms.
Pediatric Audiology: Audiologists work with children to assess and treat hearing and balance disorders, including conducting newborn hearing screenings and providing early intervention services to support development.
Counseling and Education: Audiologists offer counseling to patients and their families on hearing conservation, communication strategies, and the psychological aspects of hearing loss. They educate the community on the importance of hearing health and prevention.
Research and Development: Many audiologists engage in research to advance understanding of auditory and vestibular disorders, improve diagnostic techniques, and enhance treatment options. They contribute to innovations in hearing technology and rehabilitation methods.
Collaboration: Audiologists collaborate closely with other healthcare professionals, such as otolaryngologists (ENT specialists), speech-language pathologists, educators, and occupational therapists, to provide comprehensive care for patients with complex needs.
Audiologists typically hold a doctoral degree in audiology (Au.D.) or a related field and must be licensed or certified to practice in their jurisdiction. They work in various settings including hospitals, clinics, private practices, universities, schools, and research facilities, playing a vital role in improving the quality of life for individuals with hearing and balance disorders.